Hub Drain vs. Floor Drain | Find Your Optimal Plumbing Solution
In any commercial or residential plumbing system, drains play a crucial role in maintaining hygiene, ensuring water flow, and preventing flooding. Among the many types of drains, hub drains and floor drains often come up in discussions for specific applications.
While they might seem interchangeable at first glance, each type serves distinct purposes and functions based on design, regulations, and practical use. Choosing the right drain can save time, money, and effort in the long run by ensuring compliance with local plumbing codes and optimizing system performance.
This article will help you know the essential differences between hub drains and floor drains, their specific applications, installation requirements, and considerations for selecting the best one for your project.
What is a Hub Drain?
A hub drain is a specialized type of plumbing connection that allows water discharge from pipes or equipment directly into the drainage system. Instead of sitting flush with the floor, hub drains often feature a raised inlet designed to receive water from an indirect waste pipe.
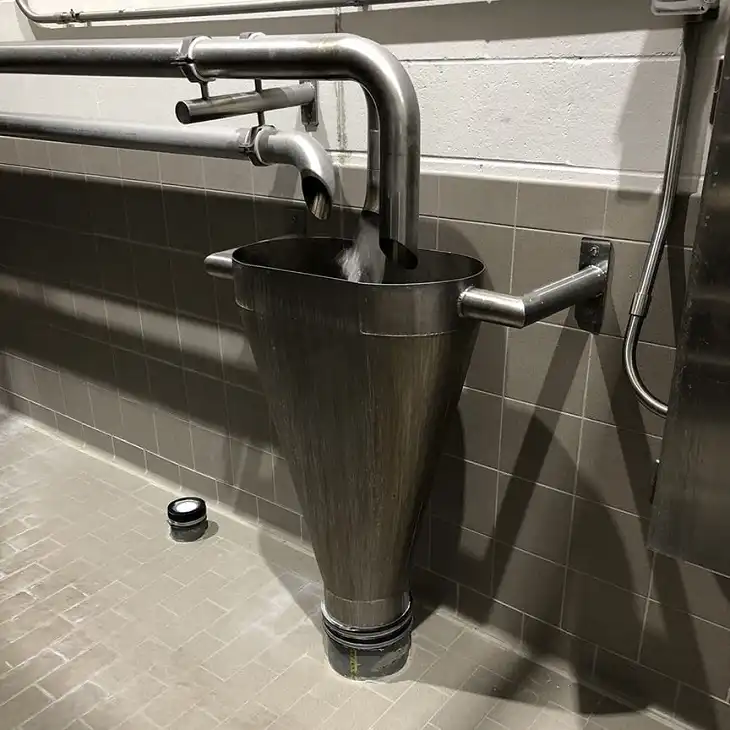

This setup helps prevent cross-contamination and ensures compliance with health and safety codes in environments where sanitary conditions are paramount.
Characteristics of a Hub Drain:
- Indirect Connection:
Hub drains typically require an indirect connection to equipment like dishwashers, ice machines, or HVAC condensate lines. The waste pipe discharges water above the drain inlet, creating an air gap that protects against backflow. - Raised Inlet:
Unlike floor drains, which are flush with the surface, hub drains have a raised inlet, reducing the risk of debris entering the drain system. - Common Applications:
- Commercial kitchens
- Healthcare facilities
- Food processing plants
- Laboratories
Hub drains are essential where stringent health codes require an air gap for backflow prevention. For example, in a restaurant kitchen, the indirect waste from a sink may flow into a hub drain to prevent contamination of potable water.
What is a Floor Drain?
A floor drain is a plumbing fixture installed flush with the floor to collect and channel water to the sewer or stormwater system. These drains are designed to handle large volumes of water and are common in areas prone to spills or frequent cleaning.

Characteristics of a Floor Drain
- Flush with the Surface:
Floor drains are typically installed level with the surrounding floor, allowing water and debris to flow directly into the drain. - Direct Connection:
Unlike hub drains, floor drains usually have a direct connection to the drainage system, which means water flows straight from the surface into the sewer line. - Grate or Cover:
Most floor drains have a grate or cover to prevent large debris from clogging the system. - Common Applications:
- Bathrooms
- Garages
- Laundry rooms
- Public restrooms
- Industrial facilities
Floor drains are indispensable in areas where standing water can cause damage, safety hazards, or sanitation issues.
What Is the Difference Between Hub Drain and Floor Drain?
The key differences that set hub drains apart from floor drains are as follows:
| Aspect | Hub Drain | Floor Drain |
| Design | Raised inlet for indirect connections | Flush with the floor for direct water flow |
| Connection Type | Indirect (air gap required) | Direct connection to sewer or stormwater line |
| Applications | Commercial kitchens, healthcare, food processing | Bathrooms, garages, public spaces, factories |
| Purpose | Backflow prevention, sanitary compliance | Handling surface water and spills |
| Grate/Cover | May or may not have a cover | Typically includes a grate to block debris |
Installation Considerations
When deciding between a hub drain and a floor drain, several factors should guide your choice:
- Building Codes and Regulations:
Local plumbing codes may dictate the use of hub drains for specific appliances and equipment to ensure backflow prevention and sanitary conditions. - Water Source and Flow Type:
If the water source involves indirect waste (e.g., from appliances), a hub drain is required. For direct surface water collection, a floor drain is more appropriate. - Maintenance Needs:
Floor drains can accumulate debris over time, necessitating regular cleaning. Hub drains, with their raised inlets, are less prone to clogging but still require inspection to maintain the air gap. - Environment and Usage:
Commercial kitchens and healthcare facilities often mandate hub drains for sanitation purposes. On the other hand, garages, bathrooms, and industrial spaces benefit from floor drains to handle surface water efficiently.
Choosing the Right Drain for Your Needs
When selecting between a hub drain and a floor drain, consider the following:
- Purpose: Are you dealing with indirect waste or surface water?
- Health and Safety: Do regulations require an air gap for backflow prevention?
- Volume of Water: Will the area experience significant water flow, necessitating a flush floor drain?
- Maintenance: Can the drain location be easily accessed for cleaning and inspection?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the standard floor drain size?
The standard size for floor drains is 4 inches in diameter. However, depending on the specific application and local plumbing codes, smaller or larger sizes may be used. It’s always best to consult local regulations and a professional plumber for guidance on the appropriate size for your project.
What is the difference between floor drain and floor trap?
A floor drain is a complete unit that includes a grate, strainer, and pipe to remove water from a floor. A floor trap, on the other hand, is a component that prevents sewer gases from entering a building, often installed beneath a floor drain or other plumbing fixtures.
Conclusion
While both hub drains and floor drains play essential roles in modern plumbing, understanding their differences is critical to choosing the right one for your needs. Hub drains offer a sanitary solution for indirect waste, making them ideal for environments where health and safety are paramount.
Floor drains, by contrast, are perfect for managing surface water and preventing flooding in various settings. Whether it’s a bustling commercial kitchen, a healthcare facility, or an industrial warehouse, the right drain will ensure efficiency, compliance, and peace of mind.






